
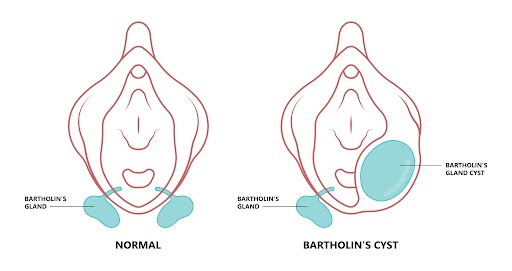
A Bartholin cyst, also known as Bartholin gland cyst, is a small fluid-filled sac that develops when the opening of a Bartholin gland is obstructed. Just below the opening of the vagina, there are two Bartholin glands, one on each side.
Bartholin cysts do not usually have other symptoms other than a lump in your vulva. It is typically painless. Most Bartholin cysts are detected through routine pelvic examinations or by the patient themselves.
Cysts that are larger may cause discomfort during sexual intercourse, walking or sitting. Even if a cyst causes no symptoms, the patient may nevertheless find it to be cosmetically unpleasant.
If the cyst gets infected, it can form an abscess. Pus-filled pockets are known as abscesses.
Bartholin abscess symptoms include:
The Bartholin glands, which are approximately 1 cm in size, produce small quantities of fluid that keeps the vulva (the area surrounding the vaginal opening) moist.
If the opening of a Bartholin gland is blocked, fluid can accumulate and form a cyst. This typically occurs in only one gland, not in both simultaneously.
It is unknown why the ducts get obstructed. However, sexually transmitted bacterial infections (STIs), such as chlamydia or gonorrhoea or other bacterial infections, such as Escherichia coli (E.coli), have been associated with this condition.
Your doctor would first question your general health and symptoms before conducting a thorough physical examination. Diagnosis is made based on your reported symptoms, physical examination, and investigations.
Should the cyst become infected, your doctor may use a swab to remove a sample of discharge. This sample will be sent for analysis to identify the bacteria responsible for the infection.
Bartholin cyst treatment depends on the cyst size, symptoms and whether it is infected (abscess). If you have no symptoms, you may not require therapy. Otherwise, treatment options include:
Sitz baths or warm baths to relieve vaginal discomfort and pain.
Hold a warm compress against the area.
Balloon catheter insertion
A small incision in the cyst is made to drain the fluid. A little balloon might be inserted into the hole to prevent it from closing entirely. The balloon is attached to a catheter that aids in the drainage of fluid from the Bartholin gland. The doctor will remove the balloon in approximately one month. It leaves a little opening through which liquid can drain.
In most cases, antibiotics are not necessary. However, it is required in some instances, especially if you have had an abscess previously or if you are at high risk for the infection to spread.
Marsupialisation
The cyst is cut open, and the fluid is drained. The treated region may be loosely packed with gauze to absorb fluid from the incision and halt bleeding once the procedure is complete. This is usually removed before you return home.
Surgery to remove the affected Bartholin gland may be recommended if other treatment options have been ineffective.
After surgery, you may be instructed to avoid the following to aid wound healing and reduce the risk of infection:
If you experience any of the symptoms of Bartholin cyst, reach out to your doctor today. An early diagnosis is effective at treating the disease.
A dedicated and expert team of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists at Pantai Hospital is available for consultation to provide the best care and assistance. Get in touch with us to book an appointment today if you have any concerns or questions regarding your reproductive health.
For health screening appointments, please contact the Health Screening Centre at your nearest Pantai Hospital.
Pantai Hospital has been accredited by the Malaysian Society for Quality in Health (MSQH) for its commitment to patient safety and service quality.

