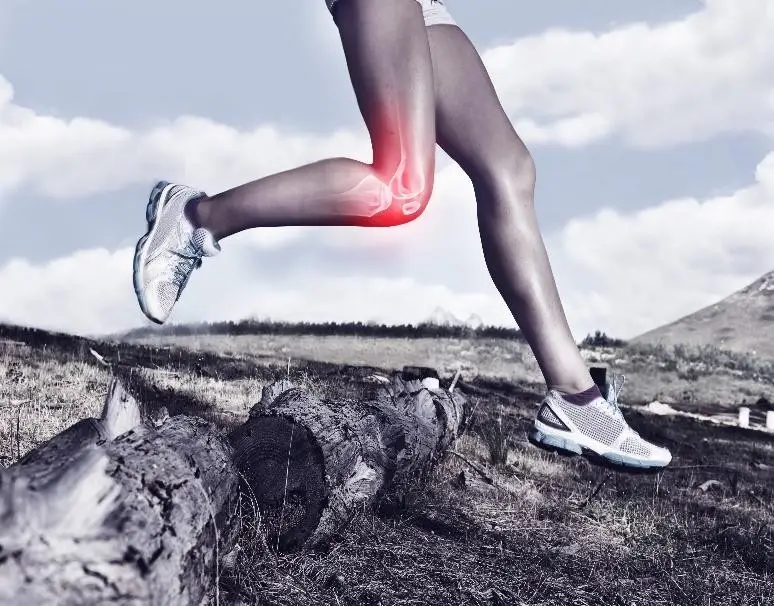


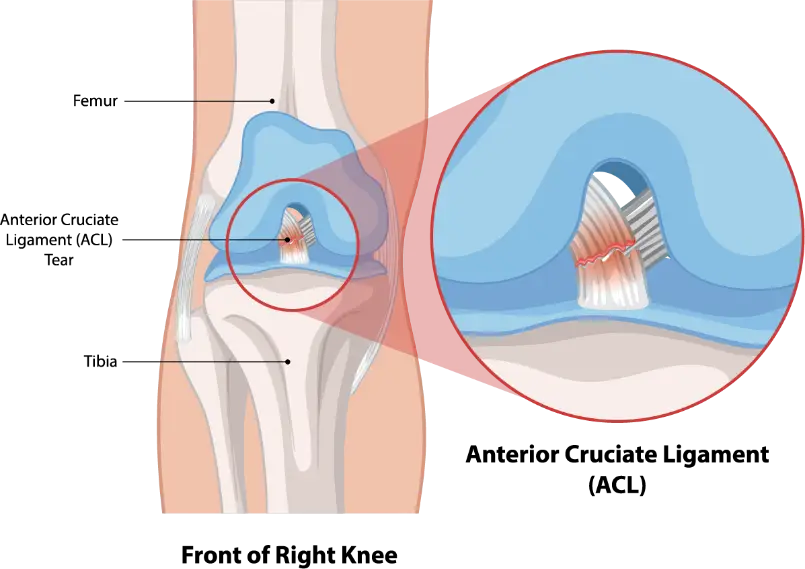
The ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) is the most commonly injured ligament in the knee, often due to sports-related activities. While an anterior cruciate ligament injury is most well-known, the knee is also supported by the posterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and lateral collateral ligament—each serving critical roles in maintaining joint stability. A torn ACL typically requires surgical repair.
Most individuals recover fully and return to their sports without long-term issues. Recovery usually takes between six to nine months.
Ligament injuries are called sprains and are classified by how serious they are:
Partial tears of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) are uncommon. In fact, most ACL tears involve complete or nearly complete tears.
Individuals who suffer an ACL injury are at a higher risk of developing osteoarthritis in the knee, even after undergoing surgical reconstruction.
Several factors may contribute to this risk, including the severity of the original injury, the presence of additional damage within the knee joint, and the individual’s level of physical activity following treatment.
ACL injuries can be managed through non-surgical or surgical methods, depending on the severity of the tear.
For minor injuries, start with the R.I.C.E. method to reduce pain and swelling:
After R.I.C.E., physiotherapy helps restore knee function, improve motion, strengthen leg muscles, and boost stability—reducing the risk of abnormal anterior tibial translation that can worsen instability.
Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction is a minimally invasive procedure done under general anaesthesia using arthroscopy (keyhole surgery). The surgeon makes small incisions to insert a camera and surgical tools. The damaged ligament tissue is removed and replaced with an ACL graft, sourced from the patient’s knee or a donor. The graft is securely attached to surrounding bones to support new ligament growth, restoring knee stability and function.
See our orthopaedic specialists if you think you have an ACL injury. If you have knee pain, swelling, or your knee feels weak or unstable after an injury, it’s important to get it checked. Early treatment can help you recover faster and avoid more damage.


