
A fracture refers to a broken bone, whereby the bone may be partially or completely cracked or broken due to falls, car accidents, sports injuries or underlying medical conditions.
Fractures can be classified into:
| Types of fracture | Description |
|
Transverse fracture 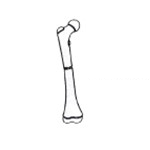
|
Horizontal fracture line. |
|
Oblique fracture 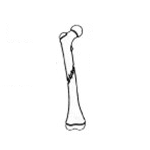
|
The bone is broken diagonally. |
|
Spiral fracture 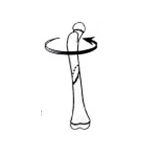
|
The fracture spirals around the bone. Commonly seen in twisting injuries. |
|
Comminuted fracture 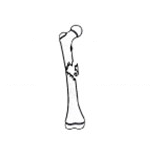
|
There are more than two fracture fragments. |
|
Segmental fracture 
|
At least two fracture lines that together isolate a bone segment. |
|
Greenstick fracture 
|
Incomplete fracture accompanied by angular deformity (like snapping a green twig). Seen in children. |
|
Impacted fracture 
|
Fracture due to impact on adjacent bone. |
|
Compression fracture 
|
A type of fracture that causes the vertebrae to collapse. |
|
Stress fracture |
A small crack or severe bruise within a bone caused by repetitive trauma. |
Bone fracture symptoms include the following:
The bone has sufficient strength and resilience to withstand a significant amount of stress despite its fragility.
A fracture occurs due to the following:
Patients with suspected fractures need prompt and, oftentimes, emergency evaluation to determine the presence of potentially life-threatening complications. Following a major trauma or significant injury, patients should go to the Emergency Department for a comprehensive evaluation immediately.
On the other hand, patients without life-threatening injuries can be assessed at the Orthopaedic clinic. Your doctor would first question your general health and symptoms before conducting a thorough physical examination. Diagnosis is made based on your reported symptoms, physical examination, and investigations.
Your doctor would request an x-ray to verify the diagnosis and determine the exact location of the fracture in the bone. When the full extent of a fracture is not apparent on an x-ray, computed tomography (CT) scan may be requested for accurate visualisation of the fracture.
The healing time for a fracture can range from several weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the injury, age of the patient, how well you follow your doctor's instructions, and other factors that influence fracture healing.
A dedicated and expert team of Orthopaedic specialists at Pantai Hospital is available for consultation to provide the best care and assistance.
Get in touch with us to Accident and Emergency (A&E) department at your nearest Pantai Hospital for major trauma.
Pantai Hospital has been accredited by the Malaysian Society for Quality in Health (MSQH) for its commitment to patient safety and service quality.

