
Maintaining mobility is essential for enhancing quality of life and ensuring good health. If left untreated, injuries to the bones or muscles may lead to serious complications.
With a team of experienced orthopaedic specialists, we offer comprehensive care for a wide range of musculoskeletal conditions. From fractures and sports injuries to degenerative diseases and complex joint issues, we are dedicated to providing personalised treatment plans tailored to each individual’s unique needs.
Arthroplasty is a surgical procedure to restore a joint’s functionality by replacing damaged bones with an artificial joint (prosthesis) made of metal, ceramic, or plastic. Your doctor may replace the whole joint (total joint replacement) or only the damaged portion of the joint (partial joint replacement).
It commonly involves the hip and knee joints, but it may less commonly involve the ankle, elbow, or shoulder joints.
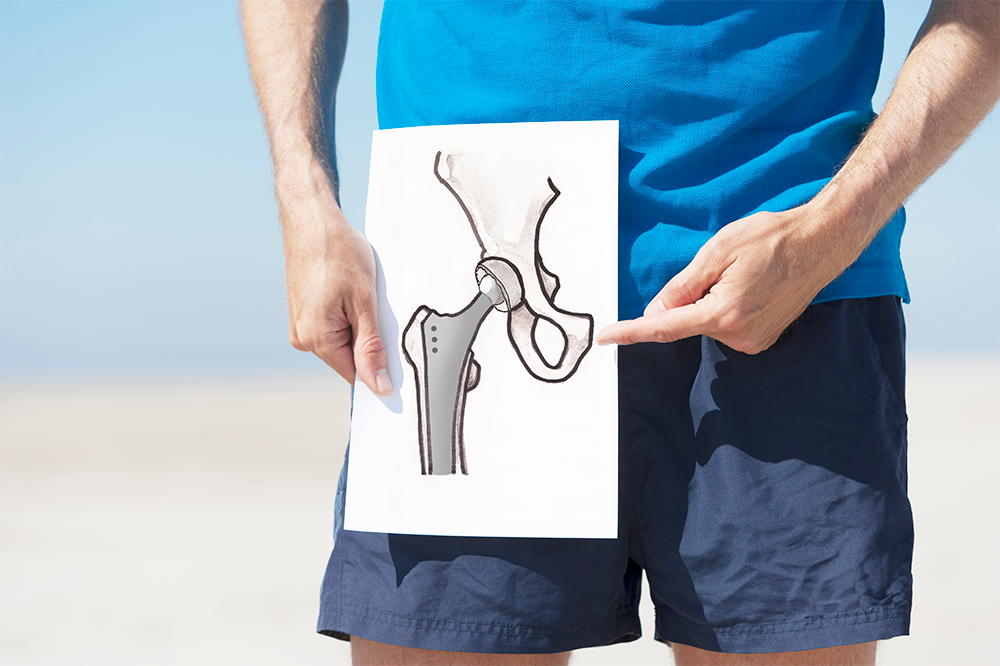
Total hip arthroplasty or total hip replacement surgery involves replacing the femur (head of the thigh bone) and the acetabulum (hip socket) with artificial joint components.
The damaged joint is replaced or reconstructed with an artificial joint (prosthesis) made of metal, ceramic, or plastic. The ball and socket are designed to glide together to replicate the hip joint.
This surgery is most likely needed when you have little pain relief from non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or if other treatments, such as physiotherapy, do not relieve hip pain.
Conditions that damage the hip joint and may warrant a hip replacement surgery include:
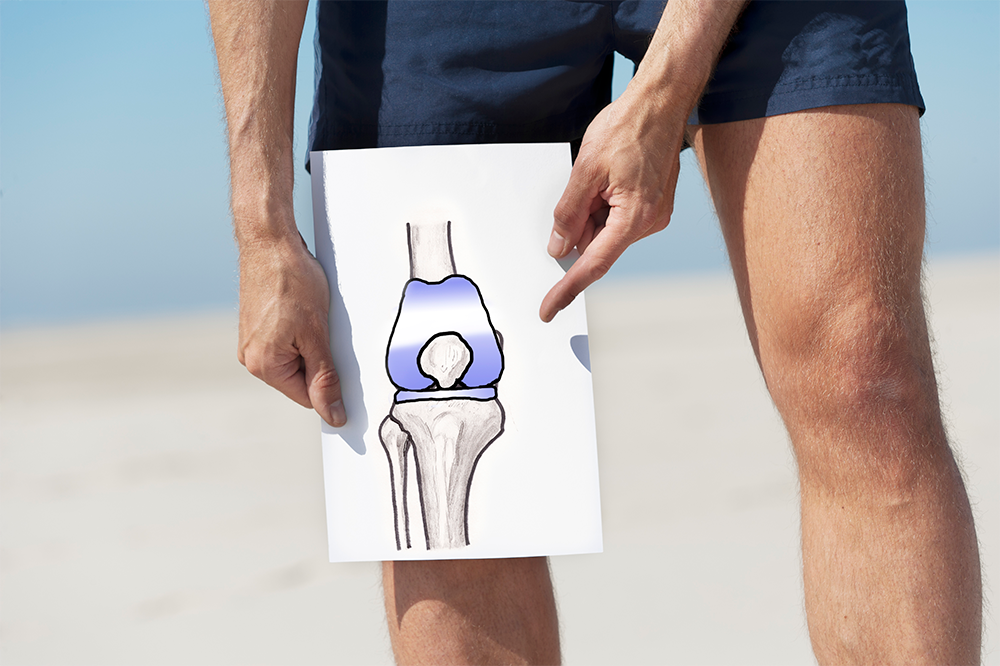
Total knee replacement surgery or total knee arthroplasty is a surgical procedure to replace the damaged part of the joint with artificial joint components (prosthesis).
The main reason for knee arthroplasty is to alleviate pain and restore functionality of the joint. This procedure is typically considered when alternative treatments like weight management, exercise, medications, injections, and bracing have not effectively reduced knee pain caused by arthritis. Replacing the painful arthritic joint with an artificial joint gives the bones new surfaces, which glide smoothly without causing severe pain.
Total knee replacement is done to replace a knee joint that is affected by a range of conditions including severe osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis disease or osteonecrosis.
Artificial knee replacement surgery is relatively common with most patients aged between 50 and 80 years. Over 90 percent of patients experience improvement in pain levels and mobility.
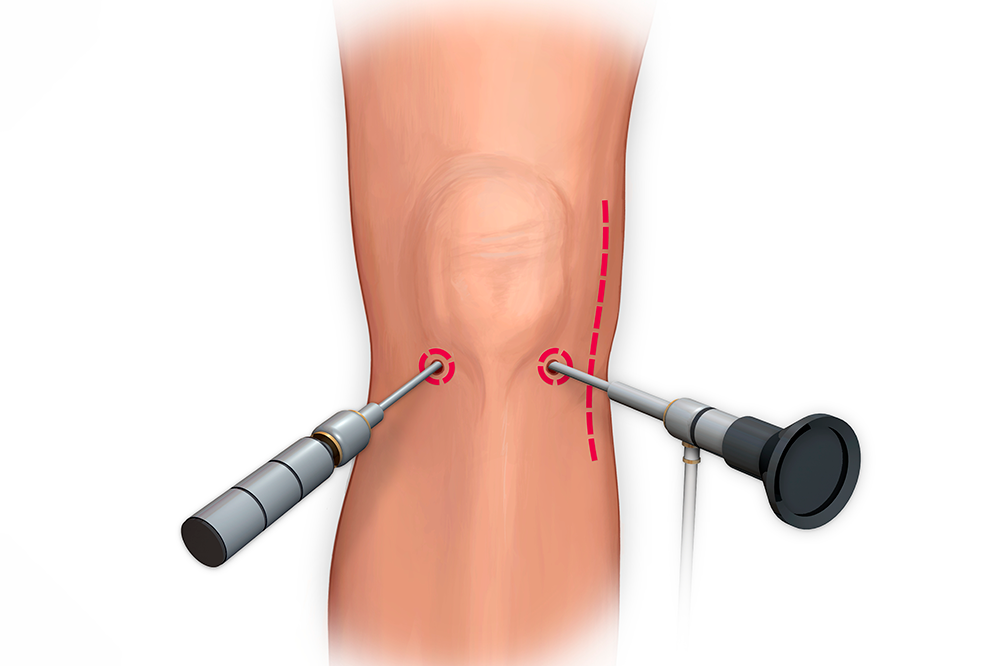
Arthroscopy is a type of keyhole surgical procedure that is used to diagnose and treat joint problems. It is commonly done for knee joints but can also be used for the ankle, hip, wrist, elbow, and shoulder joints.
Arthroscopy makes it possible for surgeons to diagnose and treat conditions such as ligament and meniscus tears in the knee, arthritis, rotator cuff tears, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
The arthroscopy procedure involves a small incision, and the insertion of a tiny camera called an arthroscope into the knee. This enables the knee surgeon to visualise the problem in the knee and, if necessary, correct the issue using small instruments through another small incision.
Find out more about Arthroplasty versus Arthroscopy.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in your hands and fingers because the median nerve is compressed and squeezed.
Carpal tunnel release is usually recommended if symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling sensation worsen, or other treatments have not improved your symptoms. This minor procedure can be performed as day surgery under local anaesthesia.
A trigger finger is a condition where one or more of the tendons in the finger are affected, making it difficult to move the finger. The affected finger may become ‘locked’ or stuck in a bent position.
Trigger Finger surgery may be suggested if other treatment options have not worked, and the affected finger is locked. There are two surgical options:
Trigger finger surgery is performed to open the pulley at the base of the finger in order to allow the tendon to glide freely. Both surgeries only require local anaesthesia, and you would be able to return home the same day.
Tendons are crucial components of the musculoskeletal system, serving as strong cords at the ends of muscles where they attach to the bone.
A tendon from one of your healthy fingers would be detached and reattached to the affected finger. This is done to restore function following muscle or tendon dysfunction due to nerve or muscle injury or neuromuscular defect.
Recent technological advances in spine surgery have allowed orthopaedic surgeons to employ minimally invasive techniques to treat back and neck conditions.
A spine osteotomy is a procedure to correct spinal deformities and restabilise the spine.
The procedures include:
A lumbar discectomy is performed to treat herniated or slipped discs in the spine. It involves the removal of the part of the disc which is exerting pressure on the nerve. This can be done as an open surgery or a minimally invasive procedure.
Decompression laminectomy or laminotomy is a procedure that relieves pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots caused by spinal stenosis. Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spinal canal, resulting in pressure on the spinal cord. This causes pain, weakness, or numbness in the back, legs, arms, and neck.
This surgical procedure removes tissue and bone, exerting pressure on the spine. It is also used to treat spinal injuries, herniated discs, and spinal tumours.
Depending on the type, location and severity of the fracture, a range of techniques are used to ensure that the bones are healing and stable to retain function. This may include immobilisation and the insertion of pins, plates, wires, and screws.
Amputation is the surgical removal of all or part of a limb or extremity, such as an arm, leg, foot, hand, toe, or finger.
Surgical removal, as in the excision of a tumour.
Non-surgical treatments that are recommended include:
A wide range of rehabilitation services are available to help individuals regain physical, mental, and life skills following injury, surgery, or other conditions that have impacted their ability to perform daily activities. The primary goal of orthopaedic rehabilitation is to improve functional ability and overall quality of life.
Physiotherapy and occupational therapy are two key components of orthopaedic rehabilitation. Physiotherapy focuses on restoring and improving physical movement and function, often targeting specific body parts or areas affected by injury or surgery. This may include exercises, manual therapy, and other techniques to improve strength, flexibility, and mobility.
Conversely, occupational therapy focuses on helping individuals return to their daily routines and activities. Occupational therapists work to improve a person’s ability to perform tasks such as dressing, bathing, cooking, and working, with an emphasis on adapting to the environment or using assistive devices to facilitate independence.
A dedicated and expert team of Orthopaedic surgeons at Pantai Hospital is available for consultation to provide the best care and assistance.
The rehabilitation team at Pantai Hospitals is trained to provide the best care for our patients. Understanding that every individual may present with different issues and symptoms, we work closely with you to develop customised treatment plans that address your specific concerns and goals.
In the event of a medical emergency, please seek immediate medical attention at the Accident and Emergency (A&E) department at your nearest Pantai Hospital.
Pantai Hospitals have been accredited by the Malaysian Society for Quality in Health (MSQH) for its commitment to patient safety and service quality.

