What Is Gout?
Gout is a health condition characterised by inflamed and painful joints. It is typically caused by the buildup of uric acid or urate crystals in the affected area. Gout is more common in men and is often associated with obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
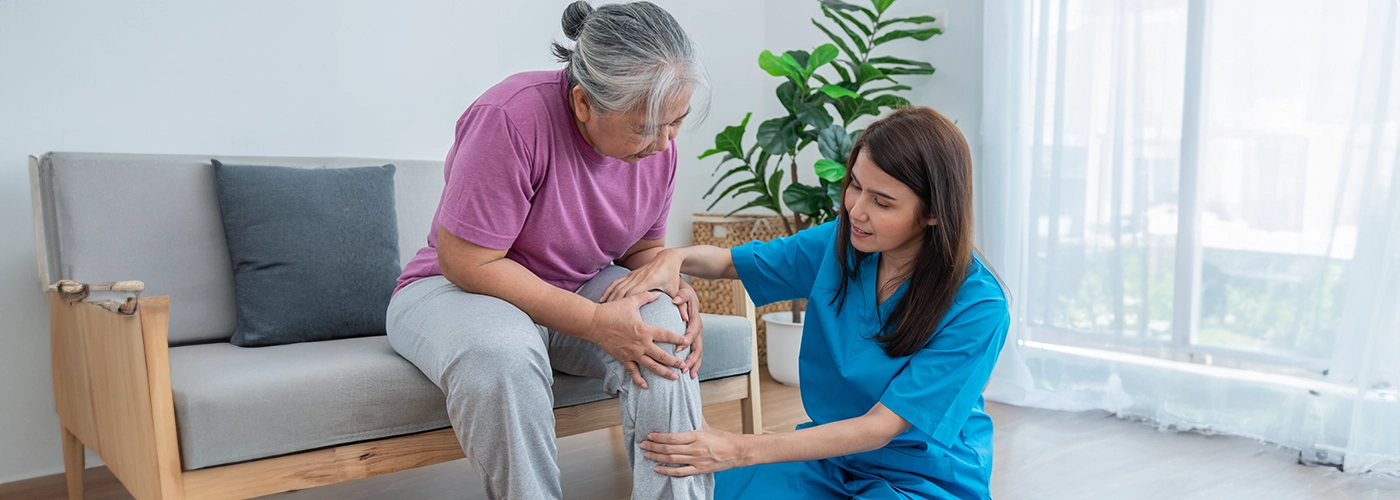
When a gout attack occurs, it usually occurs instantly and without much warning. You may feel sudden, intense pain in your affected joints. Gout can impact any joint, although it commonly affects toes, particularly the big toe joint, midfoot, ankles, knees, fingers, wrists, and elbows.
What Are the Symptoms of Gout?
Symptoms of gout include:
- Severe or intense pain in one or more joints
- Warm to touch
- Swelling in and around the affected joint
- Redness
- Joint stiffness
The symptoms can develop rapidly and last for 3 to 10 days. Recurrences of gout attacks are common among nearly all individuals, often occurring within a year after the initial episode.
What Are the Risk Factors of Gout?
You are more likely to develop gout if you have high levels of uric acid in your body. Factors that increase the uric acid level in your body include:
- Diet: Regular consumption of large amounts of meat or seafood, excessive amounts of alcohol and beverages high in sugar.
- Age and gender: Gout is more common in men, particularly those between the ages of 30 and 45. Women become more susceptible after age 55. It is also commonly seen among those older than 65, regardless of gender.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, and chronic kidney disease, are associated with an increased risk of developing gout.
Other risk factors include obesity and taking medications that affect blood levels of urate, especially diuretics.
How Is Gout Diagnosed?
If an individual experiences intermittent and sudden joint pain, followed by symptom-free periods but persistently elevated urate levels in the blood, gout is highly suspected among various conditions causing joint pain and inflammation.
Your doctor would first question your general health and symptoms before conducting a thorough physical examination. Diagnosis is made based on your reported symptoms, physical examination, and investigations.
Diagnostic tests include:
- Synovial fluid analysis: A small amount of synovial fluid is extracted from the affected joint using a needle and syringe. This fluid sample is then examined under a microscope to detect urate crystals. Additionally, tophaceous gout can be diagnosed by sampling tophi, which are deposits of urate crystals beneath the skin, using a needle.
- Blood test (uric acid test): This test measures the amount of uric acid in your blood or urine sample. Gout is usually associated with a high level of uric acid.
What Are the Treatment Options for Gout?
The objective of managing gout flares is to safely and quickly reduce inflammation, thereby reducing pain and disability. Typically, this treatment is brief and focused on addressing the duration of the flare only.
- Anti-inflammatory medication
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and indomethacin.
- Colchicine.
- Steroid medications known as glucocorticoids.
- Long-term urate-lowering therapy (ULT)
- Allopurinol and Febuxostat are recommended for recurrent attacks of gout or complications of gout.
- Lifestyle changes
- Making some positive changes to your lifestyle helps decrease your risk of having gout.
- Here are some ways you can take to change your lifestyle:
- Maintain healthy weight.
- Regular exercise.
- Avoid foods rich in purines, which contribute to uric acid production, including red meat, oily fish, seafood, and products containing yeast extract.
- Avoid sugary beverages and snacks.
- Drink more water and stay hydrated.
What Happens If Gout is Left Untreated?
Left untreated, gout can cause permanent joint damage. Some individuals with gout may experience other health problems, including:
- Chronic gouty arthritis and joint deformity, which changes the shape of your joint.
- Tophi, the plural form of tophus, is a buildup of uric acid in the joints and soft tissue.
- Kidney damage.
- Increased cardiovascular disease risk.
Untreated gout can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and increase the risk of long-term complications. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention and follow appropriate treatment and lifestyle measures to manage the condition effectively.
Make an Appointment at Pantai Hospitals
Speak to our doctors if you are experiencing symptoms of gout. A dedicated and expert team of rheumatologists at Pantai Hospital is available for consultation to provide the best care and assistance.
Get in touch with us to book an appointment today if you have concerns or questions regarding gout. We assure you the best possible care tailored to your specific needs.
Pantai Hospital has been accredited by the Malaysian Society for Quality in Health (MSQH) for its commitment to patient safety and service quality.

 Request an Appointment
Request an Appointment.webp?sfvrsn=276ce14_1/vector-(3).webp) International Patient
International Patient

.webp)


 Find A Doctor
Find A Doctor


.png?sfvrsn=71934c60_8)
.png?sfvrsn=1370dfbd_9)